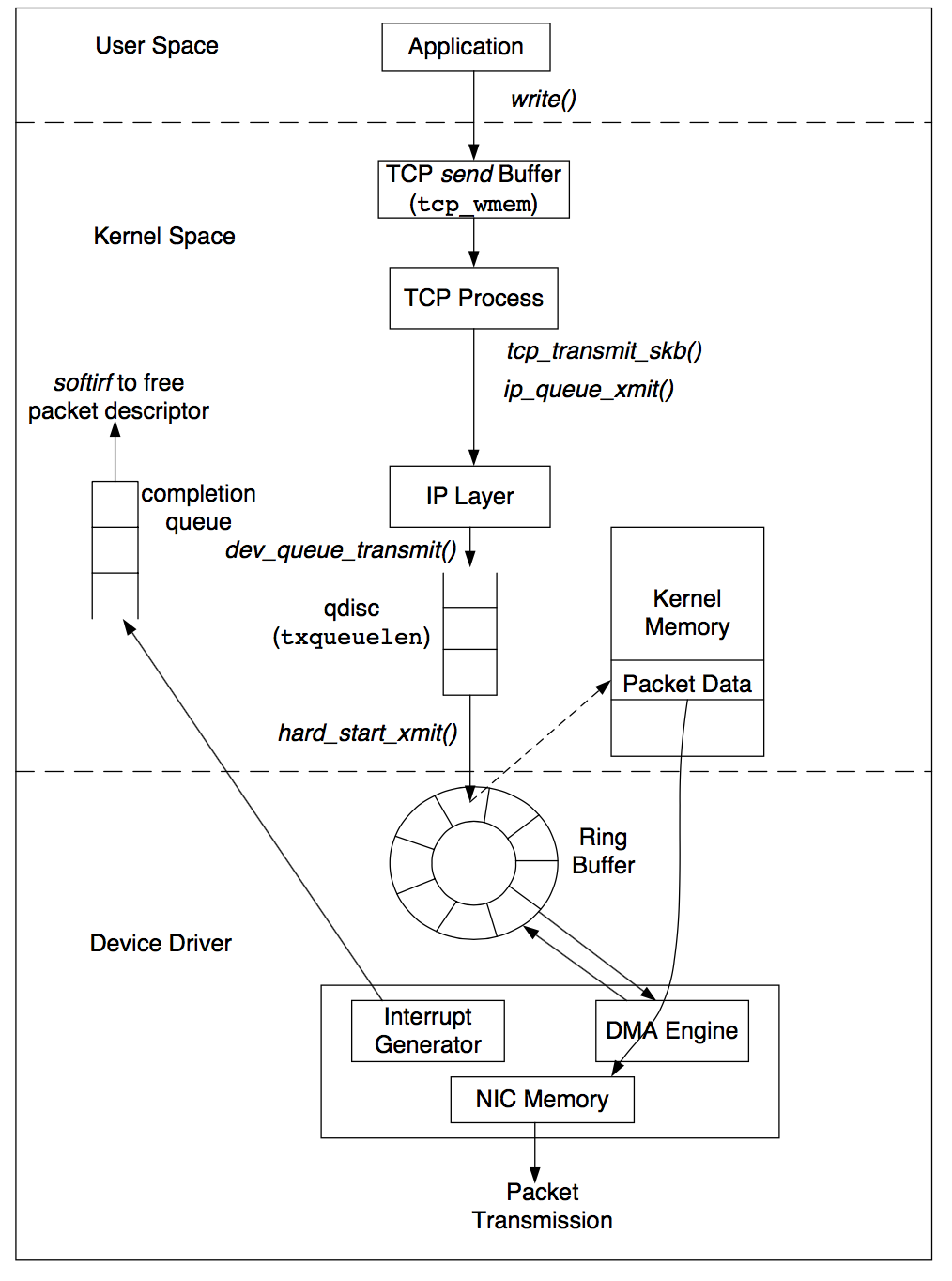
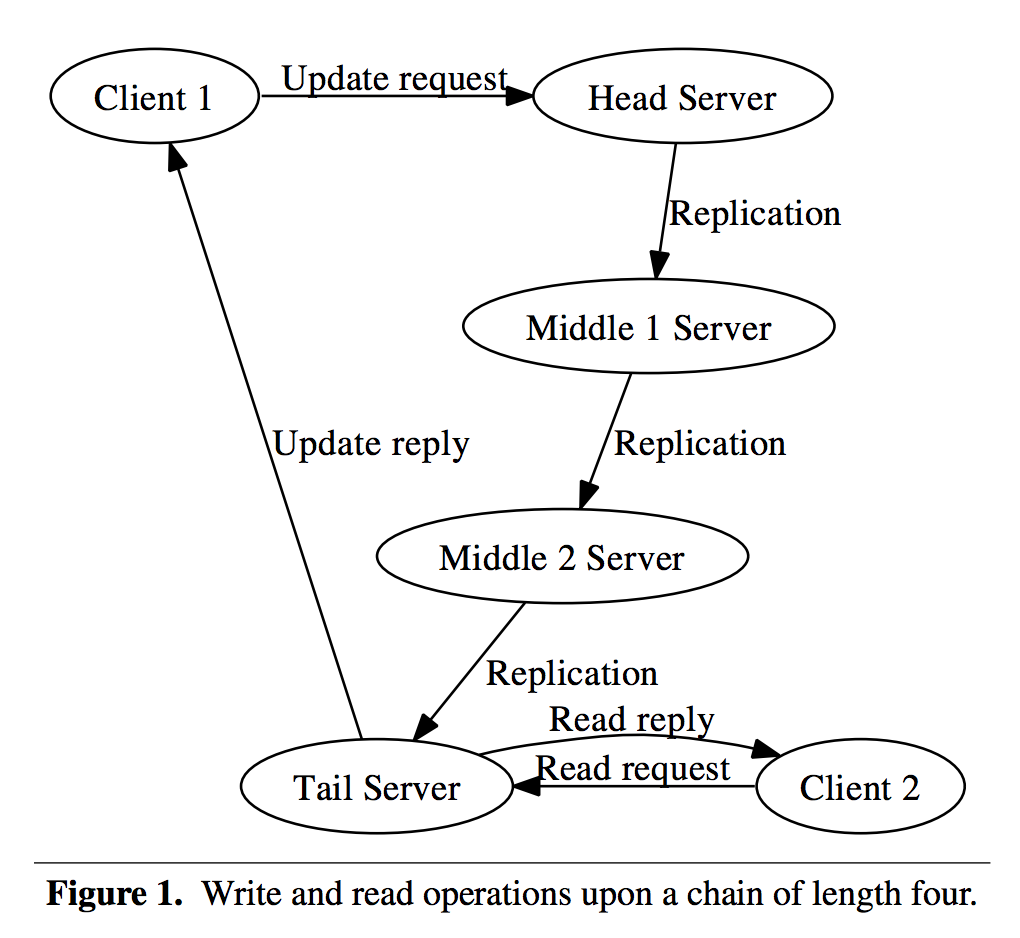
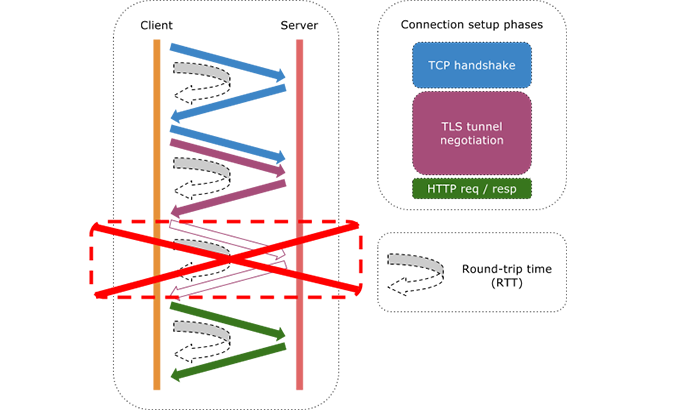
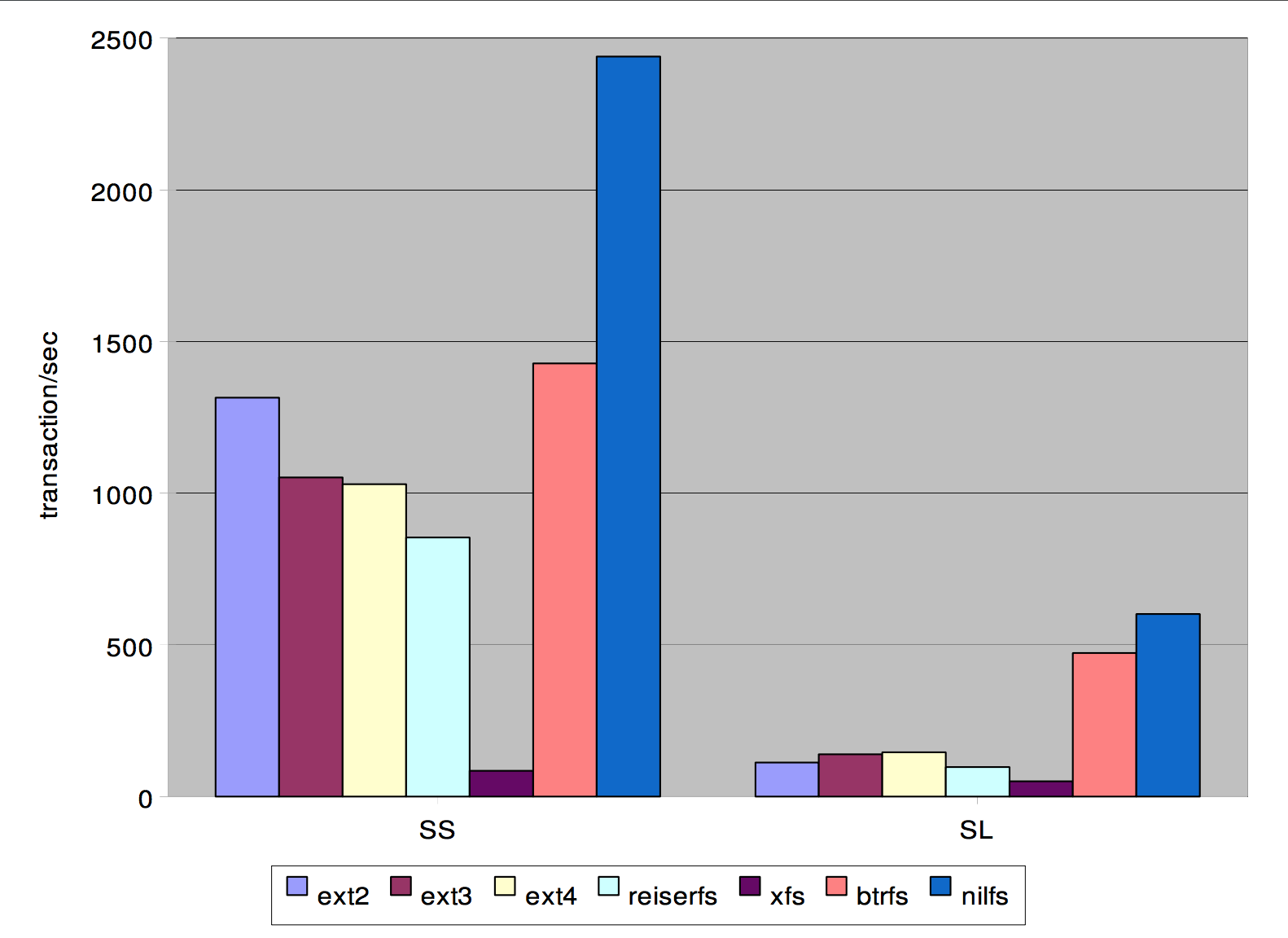
Primer Log entry = (Term, Index, Command)
Components
FSM
LogStore
StableStore
CurrentTerm
LastVoteTerm
LastVoteCand
SnapshotStore
PeerStore
RPC Protocol msgpack serializer
AppendEntries
Term
Leader
PrevLogIndex, PrevLogTerm
LeaderCommitIndex
[]Log
Term, Index
Type
LogCommand
LogAddPeer
LogRemovePeer
LogNoop
LogBarrier
RequestVote
Term
LastLogIndex, LogLogTerm
InstallSnapshot
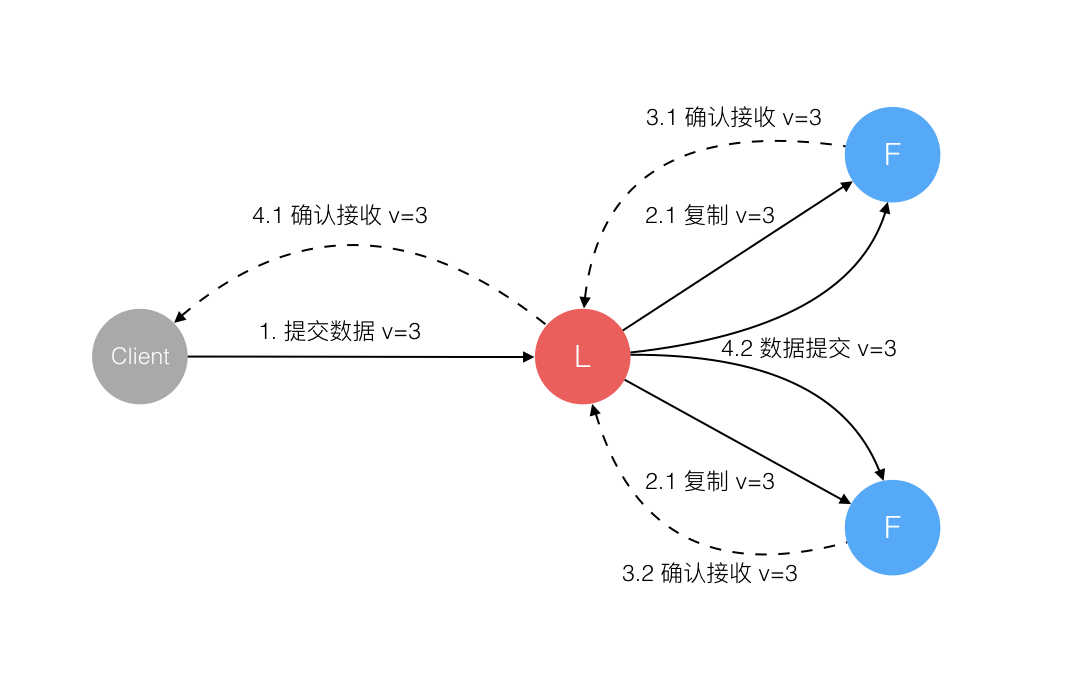
2PC Leader’s log is ‘the truth’
2.1是第一次AppendEntries,3.1后Leader apply to local FSM并update commit index,就可以向client返回了
When the Commit Index is updated, the node will pass all commands between the new and old Commit Index to the state machine.
phase2的作用:1
2
3
4
5
A(leader),B,C,D,E 5个节点,partition成A(leader)/B,C(leader)/D/E
A: apply(set x=9)
C: apply(set x=8)
由于只与leader(A)心跳,B并不知道已经partition了。如果没有phase2,B会直接更改FSM,造成consensus失败
partition修复后,A会退位成follower,同时A/B的(set x=9)这个log entry会回滚
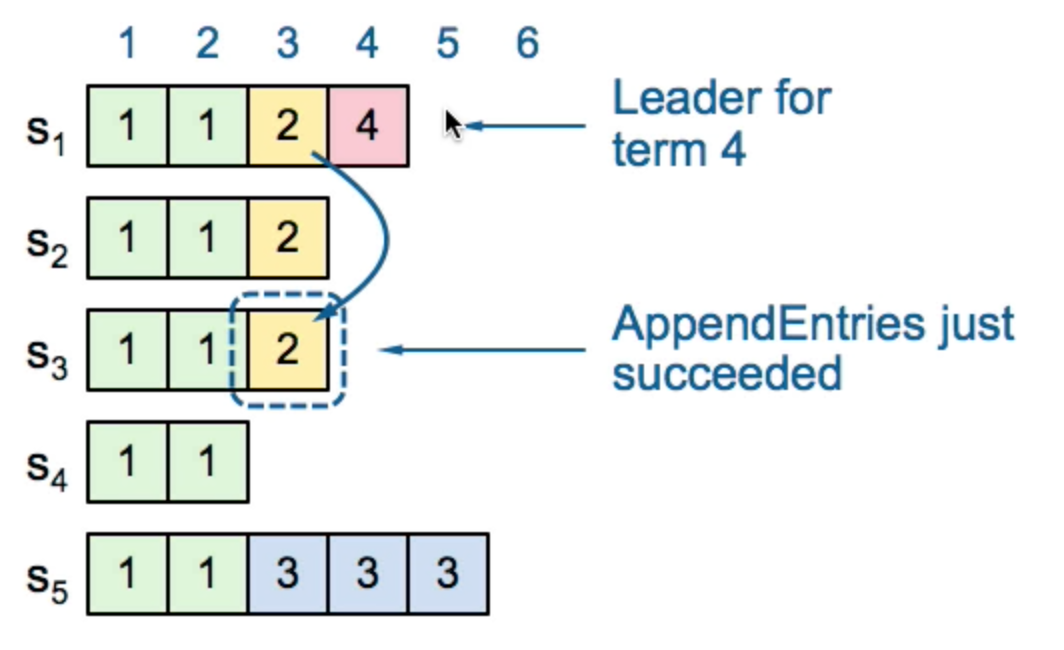
Commit For a leader to decide an entry is committed
must be stored on majority
at least one new entry from current term must also be stored on majority
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1) (term2, index3),S1 leader,index3收到S2的ack,但没收到S3的ack
即S3.LastIndex=2,此时S1 crash
2) S5成为term3 leader(S3,S4 vote for it)
term3内S5有3条append,但由于partition了,其他机器term=3
此时重新选举,S1成为term4 leader
3) S1恢复,成为term4 leader,并把(term3, index3)发给S3。
此时,不能认为(term2, index3)是可以安全commit的
因为,如果此时S1 crash,currentTerm(S2,S3)=2
S5可能成为term4 leader,'committed' log lost
4) 但如果S1在term4内有一个majority ack的log entry
(term2, index3)就可以安全commit,因为majority currentTerm=4
那样,S5不不可能成为leader
Election leader要给peers发心跳,阻止新选举(如果一直没有Apply,多久发心跳?)
处理RequestVote RPC1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
// 同一个term,只会有一个leader,但由于partition的存在,可能存在多个leader在不同的term:新的leader的term更高
if req.Term < r.getCurrentTerm() {
// rejected
return
}
if req.Term > r.getCurrentTerm() {
// Ensure transition to follower
r.setState(Follower)
r.setCurrentTerm(req.Term)
}
// 每个server只会给每个term投一票,按照先来先给原则
lastVoteTerm := r.stable.GetUint64(keyLastVoteTerm)
if req.Term == lastVoteTerm {
return
}
// 保证被选为新leader的server拥有所有的已经committed的log entry
lastIdx, lastTerm := r.getLastEntry()
if lastTerm > req.LastLogTerm {
return
}
if lastTerm == req.LastLogTerm && lastIdx > req.LastLogIndex {
return
}
// 每次投票要持久化
r.persistVote(req.Term, req.Candidate)
resp.Granted = true // 同意
Replication leader保存每个followerReplication状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
type followerReplication struct {
currentTerm uint64
matchIndex uint64
nextIndex uint64 // AppendEntries时,通过nextIndex--来truncate conflict,直到找到同步点
// 初始值是 1 + LastLogIndex(leader)
lastContact time.Time
}
Repair follower logs
delete extraneous entries
fill in missing entries
startup 1
2
3
4
5
6
从StableStore里取currentTerm,并设置当前term
从LogStore里取last Log,并设置lastLogIndex/lastLogTerm
从PeerStore取peers
进入Follower状态
restoreSnapshot: 通过SnapshotStore取snapshot,并调用FSM.Restore
启动3个goroutine: run(runFollower/runCandicate/runLeader)/runFSM/runSnapshot
runFSM 1
2
执行FSM的3个方法
Apply, Restore, Snapshot
runLeader 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
r.leaderCh <- true
// 启动每个peer(除了自己)的异步复制goroutine
for _, peer := range r.peers {
r.startReplication(peer)
}
先发送一个AppendEntries(AddPeer)当做noop心跳
// leader loop
for r.getState() == Leader {
select {
case rpc := <-r.rpcCh:
r.processRPC(rpc)
case <-r.stepDown:
r.setState(Follower)
case <-r.commitCh: <--------------------------+
r.processLogs |
case log := <-r.applyCh: |
r.dispatchLogs { |
// 先写本地 |
// 如果失败,就step down Follower |
LogStore.StoreLogs(logs) |
|
// 再复制给followers |
// inflight在获得majority的时候会通知r.commitCh
inflight.StartAll(logs)
notify each follower replication goroutine
}
case <-lease:
// 如果LeaderLeaseTimeout内没有contact quorum
// 就step down to Follower
case <-r.shutdownCh:
return
}
}
appendEntries RPC 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
func appendEntries(rpc RPC, a *AppendEntriesRequest) {
// 每次执行,无论成功失败,都要给回复
defer rpc.Responde(resp)
// 比我的term小,reject
if a.Term < r.getCurrentTerm() {
return
}
if a.Term > r.getCurrentTerm() || r.getState() != Follower {
r.setState(Follower)
a.setCurrentTerm(a.Term)
resp.Term = a.Term
}
r.setLeader(a.Leader)
// log conflict detection
if a.PrevLogEntry > 0 {
取得本地a.PrevLogEntry上的Log,并比较a.PrevLogTerm与Log.Term是否相同
如果不同,那么表示log conflict, return
}
// 处理a.Entries
//
// 1 2 3 4 5
// x y z local Logs
// o p q w a.Entries
r.logs.DeleteRange(2, 3) 因为冲突
r.logs.StoreLogs(a.Entries)
// 处理piggyback phase2的commit
if a.LeaderCommitIndex > 0 && a.LeaderCommitIndex > r.getCommitIndex() {
}
}
runCandidate 1
2
electSelf
中间,可能会收到RPC,也可能会SetPeers
Configuration Change 采用2PC方法: C_old -> C_old+new -> C_new
http://zookeeper.apache.org/doc/trunk/zookeeperReconfig.html
Q & A time 1
2
broadcast time << election timeout << MTBF
[T, 2T]
为什么每个node上的current term需要持久化? It is best guess, persistent for recovery after crash.
恢复时,从leader拿不行吗?
为什么每个node上的votedFor要持久化? 为了保证election safety: allow at most one winner per term
成为leader后,立刻发heartbeat还是等heartbeat timeout? 如果一个follower的AppendEntries失败,leader怎么处理? 一直retry,Leader’s log is ‘the truth’.
但在client方面,就没有保障了:
Engineering Config HeartbeatTimeout = ElectionTimeout = 1s
Group Commit 0 < MaxAppendEntries <= 1024
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
newLog := <-r.applyCh
ready := []*logFuture{newLog}
for i := 0; i < r.conf.MaxAppendEntries; i++ {
select {
case newLog := <-r.applyCh:
ready = append(ready, newLog)
default:
break
}
}
Lease 除了follower通过被动接受心跳来检测leader存活,leader本身也通过与majority follower
Pipeline 仅仅用于AppendEntries,通过channel实现多次发送RPC给follower而不等待response
max outstanding AppendEntries RPC calls = 128
Limitations
Apply([]Log)
StableStore.GetUint64
LeaderCh() might lose event
Paxos
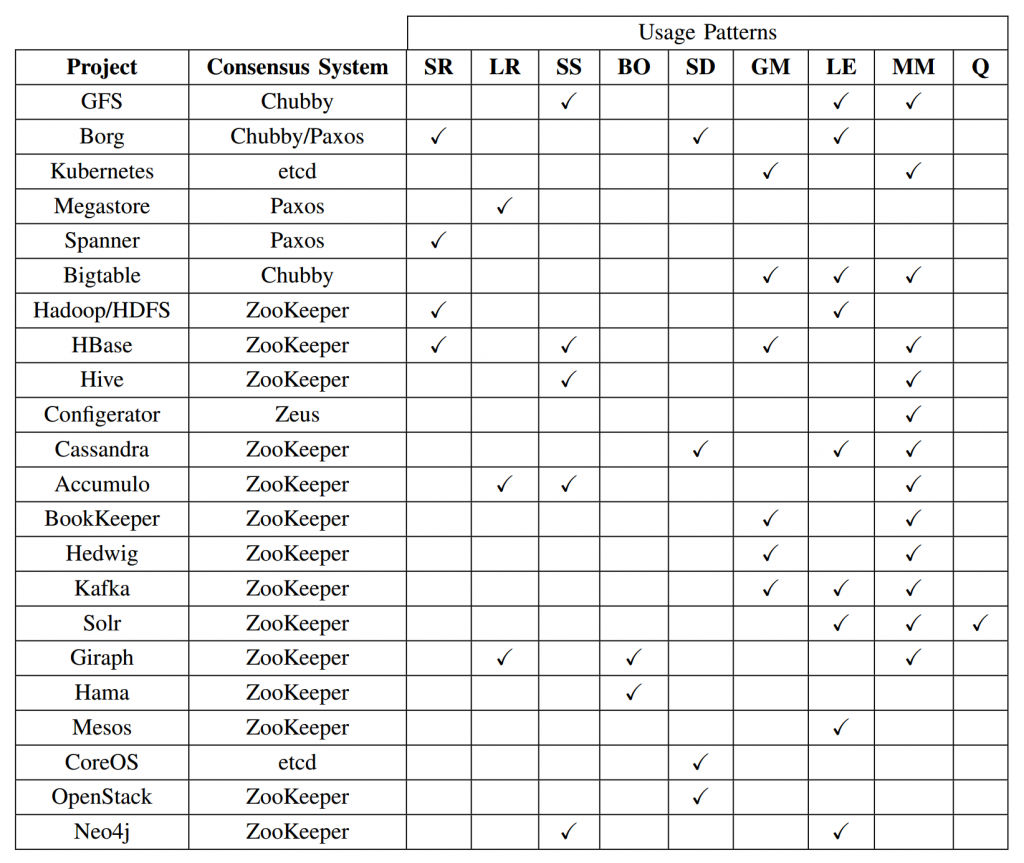
server replication (SR), log replication (LR), synchronisation service (SS), barrier orchestration (BO), service discovery (SD), leader election (LE), metadata management (MM), and Message Queues (Q).
CAP 证明:
References 1985 FLP Impossibility Result
http://www.cnblogs.com/foxmailed/p/3418143.html http://raftuserstudy.s3-website-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/study/raft.pptx
http://www.read.seas.harvard.edu/~kohler/class/08w-dsi/chandra07paxos.pdf https://www.cse.buffalo.edu//~demirbas/publications/cloudConsensus.pdf http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/techreports/UCAM-CL-TR-857.pdf