触发器的缺陷
- 如何监控
- 代码的版本控制
- test
- 部署
- 性能损耗
- 多租户
- 资源隔离
- 无法频繁发布,如何应付频繁的需求变更
触发器的缺陷
物化试图,可以理解为cache of query results, derived result
觉得用“异构表”可能更贴切
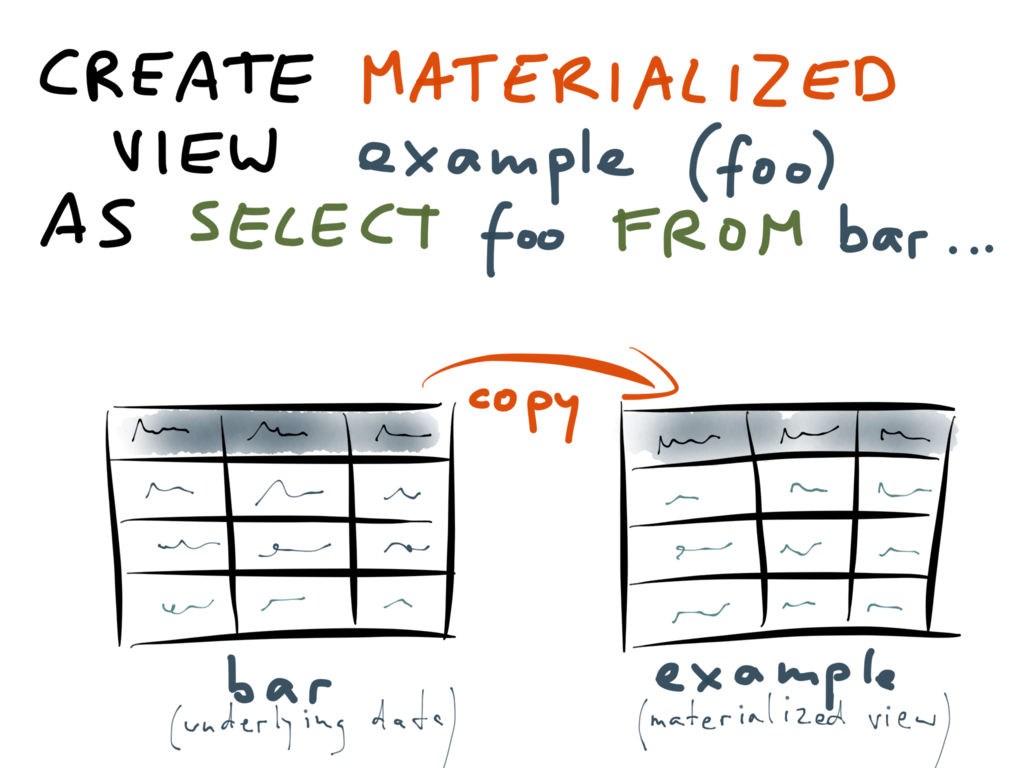
与试图不同,它是物理存在的,并由数据库来确保与主库的一致性
它是随时可以rebuilt from source store,应用是从来不会更新它的: readonly
MySQL没有提供该功能,但通过dbus可以方便构造materialized view
PostgreSQL提供了materialized view
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/materialized-view
|
|
如果需要的只是eventaul consistency,那么通过dbus来进行cache invalidation是最有效的
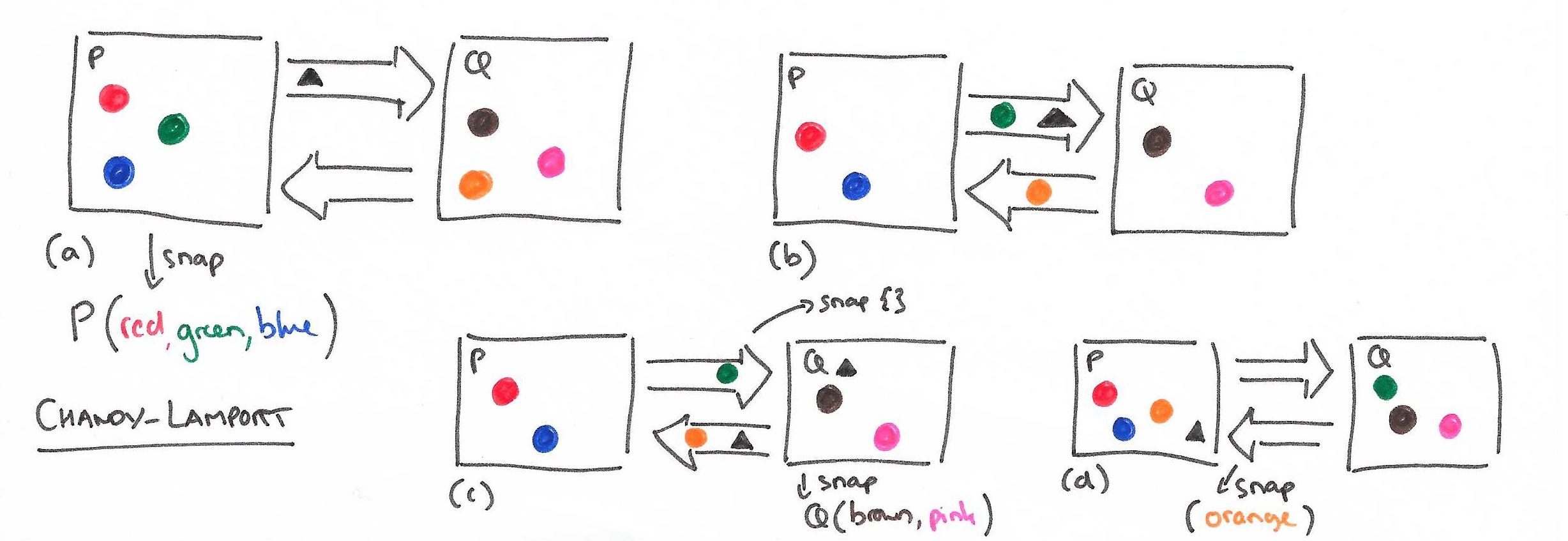
如何给分布式系统做个全局逻辑一致的快照?
Node State + Channel State
|
|
|
|
|
|
发起global distributed snapshot的节点,可以是一台,也可以多台并发
所有节点上都完成了snapshot
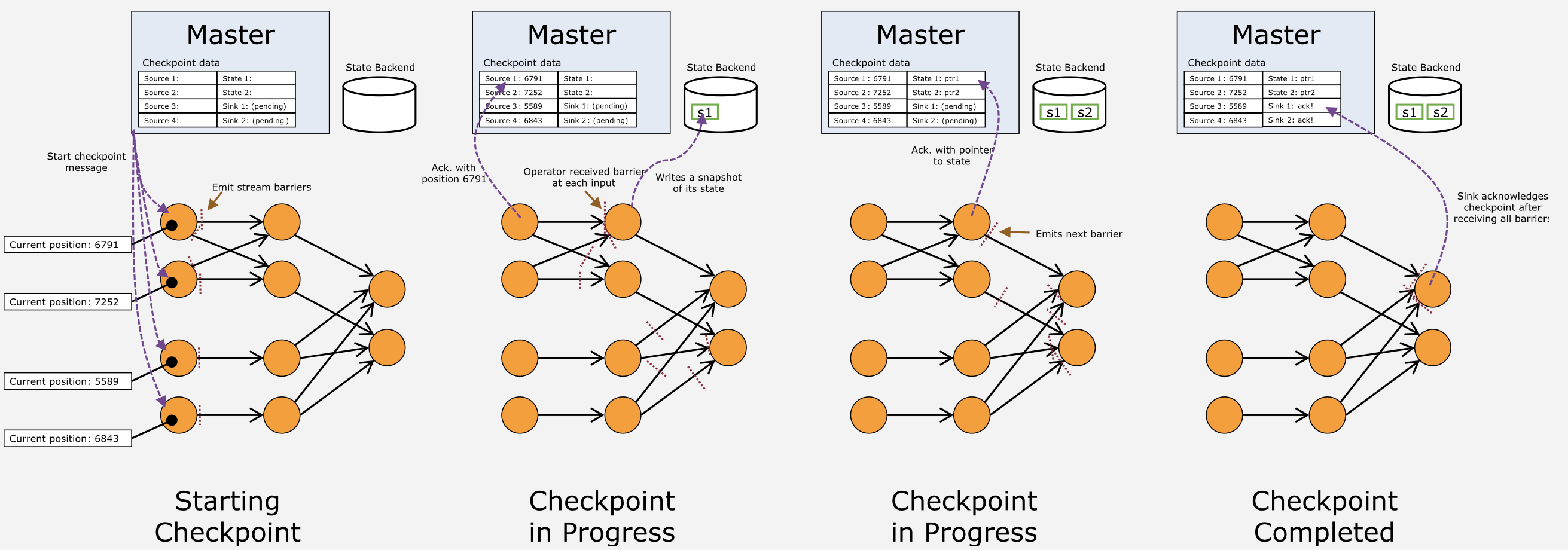
故障恢复
与Apache Storm的基于记录的ack不同,Apache Flink的failure recovery采用了改进的Chandy-Lamport算法
checkpoint coordinator是JobManager
data sources periodically inject markers into the data stream.
Whenever an operator receives such a marker, it checkpoints its internal state.
http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/um/people/lamport/pubs/chandy.pdf
https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.08603
https://ci.apache.org/projects/flink/flink-docs-master/internals/stream_checkpointing.html
https://github.com/StephanEwen/flink-demos/tree/master/streaming-state-machine
curl https://baidu.com
How the 270ms passed
分布式事务,为了性能,目前通常提供SI/SSI级别的isolation,通过乐观冲突检测
而非2PC悲观方式实现,这就要求实现事务的causality,通常都是拿逻辑时钟实现total order
例如vector clock就是一种,zab里的zxid也是;google percolator里的total order算是
另外一种逻辑时钟,但这种方法由于有明显瓶颈,也增加了一次消息传递
但逻辑时钟无法反应物理时钟,因此有人提出了混合时钟,wall time + logical time,分别是
给人看和给机器看,原理比较简单,就是在交互消息时,接收方一定sender event happens before receiver
但wall time本身比较脆弱,例如一个集群,有台机器ntp出现问题,管理员调整时间的时候出现人为
错误,本来应该是2017-09-09 10:00:00,结果typo成2071-09-09 10:00:00,后果是它会传染给集群
内所有机器,hlc里的wall time都会变成2071年,人工无法修复,除非允许丢弃历史数据,只有等
到2071年那一天系统会自动恢复,wall time部分也就失去了意义
要解决这个问题,可以加入epoch
修复2071问题时,只需把epoch+1