Basics
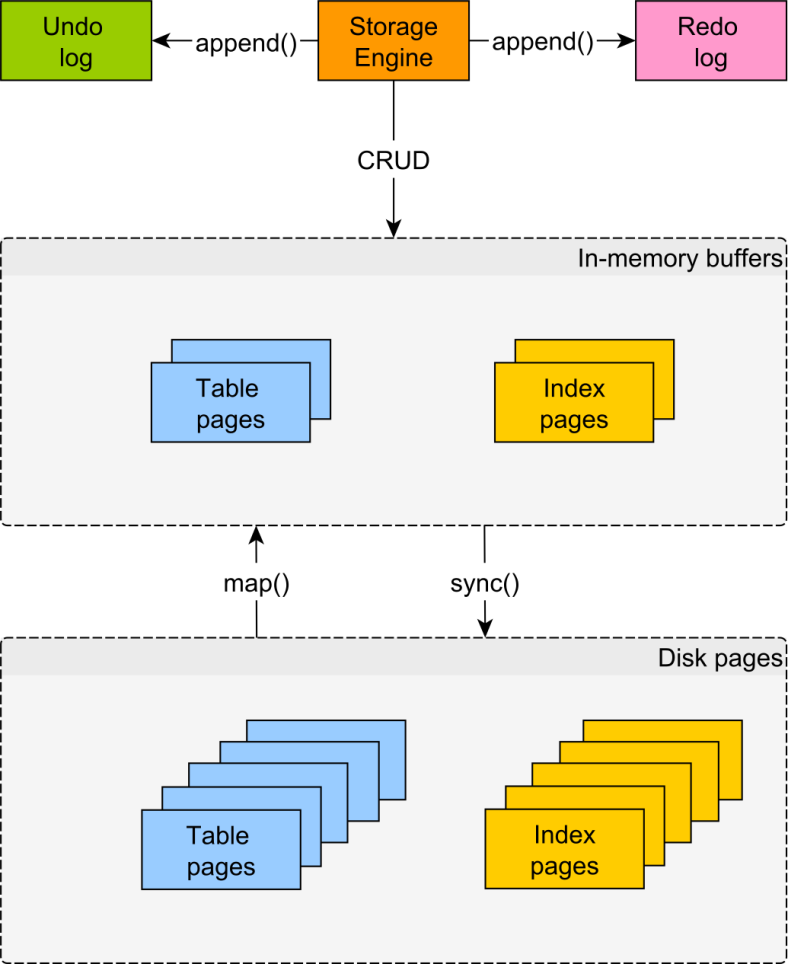
Undo log
- Oracle和MySQL机制类似
- MS SQL Server里,称为transaction log
- PostgreSQL里没有undo log,它通过mvcc系统表实现,每一行存储多个版本
Redo log
- Oracle和MySQL机制类似
- MS SQL Server里,称为transaction log
- PostgreSQL里称为WAL
Query Optimization
大部分是基于Selinger的论文,动态规划算法,把这个问题拆解成3个子问题
- cost estimation
以I/O和CPU的成本衡量 - relational equivalences that define a search space
- cost-based search
Concurrency Control
Gray论文
- 区分细粒度和粗粒度的锁
数据库是个分层结构 hierarchical structure - 提出了多种隔离级别
最初都是2PL实现的serializable isolation
Database Recovery
IBM的ARIES算法(1992),Algorithm for Recovery and Isolation Exploiting Semantics
ARIES can only update the data in-place after the log reaches storage
确保在恢复时,已经commit的事务要redo,未commit的事务要undo
redo log是物理的,undo log是逻辑的
No Force, Steal
- database need not write dirty pages to disk at commit time
由于有redo log,update pages are written to disk lazily after commit
No Force - database can flush dirty pages to disk at any time
由于有undo log,uncommitted(dirty) pages can be written to disk by the buffer manager
Steal
ARIES为each page保存LSN,disk page是数据管理和恢复的基本单位,page write是原子的
ARIES crash recovery分成3步
- analysis phase
从前向后,determine winners & losers - redo phase
如果是Force(在commit前刷dirty pages),就不需要redo stage了
repeat history - undo phase
从后向前,undo losers
ARIES数据结构
- xaction table
- dirty page table
- checkpoint
Example
ARIES是为传统硬盘设计的,顺序写,但成本也明显:修改1B,需要redo 1B+undo 1B+page 1B=3B
what if in-place update with SSD?
分布式
mid-1970s 2PC 一票否决
References
https://blog.acolyer.org/2016/01/08/aries/
http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~swanson/papers/SOSP2013-MARS.pdf
https://www.cs.berkeley.edu/~brewer/cs262/Aries.pdf